 2025-02-28
2025-02-28
 186
186导语 Introduction
本期“气候与海洋”为所有内容,不论是治理和管理层面的海洋保护还是可持续利用海洋资源(蓝色经济),提供了关键的背景。关于处理海洋跟气候变化的复杂关系有两种不同的思路。一种是通过保护海洋现有的生物多样性,利用其自然的过程来封存二氧化碳,另一种是更加主动的干预海洋的生物化学过程,从而实现更有效地封存二氧化碳、缓解气候变化及其对海洋生物多样性的压力。第一种思路注重平衡海洋生物多样性和气候的关系,而后一种出于应对气候变化的紧迫性在短期内更强调气候变化的减缓,尽管长期来看其也可以贡献于生物多样性。两种方式并不是互斥的,生物多样性更加丰富的地区可以在兼顾渔业资源利用的同时尽可能通过保护来利用生态系统的碳收集和封存功能,而其他地区则可以在充分评估风险的前提下开发人工干预的措施。《BBNJ协定》的划区管理工具和环境影响评价分别都可以应用在这两种思路的落实上。这一协定目前处于签订和生效之间过渡阶段。明年如果能达到60个国家批准的生效门槛,全球海洋治理就又能前进一步。
The “Climate and Oceans” section of this issue provides the critical context for all that follows, whether it is marine conservation at the governance and management level or the Blue Economy. There are two different rationales on addressing the complex relationship between the oceans and climate change. One is to utilize the natural processes of the oceans to sequester carbon dioxide by protecting the existing biodiversity, while the other is to intervene more proactively in the biochemical processes of the oceans to achieve more effective sequestration of carbon dioxide and mitigation of climate change and its pressures on marine biodiversity. The relationship between marine biodiversity and climate in the first rationale is relatively balanced, while the latter places more emphasis on climate change mitigation out of the urgency of addressing climate change in the short term, although it can also contribute to biodiversity in the long term. The two approaches are not mutually exclusive; in areas of greater biodiversity, the carbon capture and sequestration functions of ecosystems should be utilized as much as possible through conservation while accommodating the use of fisheries resources. In other areas, artificial interventions can be developed with a comprehensive assessment of their risks. The area-based management tools and environmental impact assessments of the BBNJ Agreement can be applied to the implementation of these two approaches, respectively. The Agreement is currently in a transitional phase between adoption and entry into force. If the threshold of 60 ratifications for entry into force is reached next year, global ocean governance will benefit from another step forward.
气候与海洋
关键点
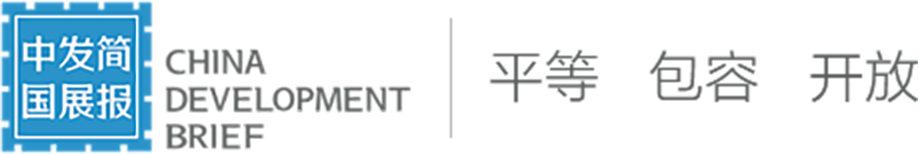
- 海水温度异常升高导致了近期的第四次全球珊瑚白化事件,全球约77%的珊瑚礁区域经历了白化级别的热应激,是有记录以来最严重的一次,对珊瑚礁生态系统构成严重威胁。
- 根据《海洋科学年度综述》,应对气候变化对海洋生物多样性的威胁,需要制定策略以增强海洋基础物种的韧性并确保其提供的生态系统服务的持续性。
- 根据《通讯·地球与环境》,由于全球变暖的影响,未来在太平洋形成的大气河流到达北美西海岸时可能会(如通过大量降雨)导致沿海岸线的海平面上升200%,可能会给加利福尼亚海岸的社区带来灾难性的影响。
泰国涛岛周围的白化珊瑚|Lillian Suwanrumpha/AFP via Getty Images
1)【解读】全球珊瑚白化事件现已成为有记录以来最大的一次
珊瑚礁维持着多样化的沿海海洋物种群落,并减轻强风暴的影响,对全球渔业至关重要。珊瑚白化会导致珊瑚礁更容易受到水污染等威胁。第四次全球珊瑚白化事件是有纪录以来最大规模的白化事件,这次白化事件从2023年1月1日持续到10月10日,全球约77%的珊瑚礁区域经历了“白化级别的热应激”。2023年2月以来,全球已有74个国家和地区报告了大规模珊瑚白化。这次全球珊瑚白化打破了之前最大规模的珊瑚白化的规模记录,超过后者11.3%,并且只用了后者形成的一半时间。究其原因,当时热带太平洋的强烈厄尔尼诺现象和长期的人类活动共同推动了海洋温度的上升,使全球海洋温度首次飙升至最高水平。尽管珊瑚可以在短暂的白化事件后恢复,但长期的热应激会导致其死亡。美国国家海洋与大气管理局(NOAA)已将加勒比海部分地区的珊瑚白化威胁等级提高到5级,这是一个新的最高等级,意味着该地区的珊瑚面临“接近完全死亡”的风险。
【Interpretation】Global coral bleaching event is now the largest on record
Coral reefs are crucial to global fisheries, as they support diverse coastal marine species communities and mitigate the impact of severe storms. However, coral bleaching makes reefs more vulnerable and susceptible to threats such as water pollution. The fourth global coral bleaching event is the largest recorded bleaching event to date. This bleaching event lasted from January 1, 2023, to October 10, 2023, with approximately 77% of coral reef areas worldwide experiencing "bleaching-level thermal stress." Since February 2023, 74 countries and regions around the world have reported large-scale coral bleaching. This global coral bleaching has broken the previous record for the largest scale of coral bleaching, exceeding the latter by 11.3%, and it took only half the time. At that time, the intense El Niño phenomenon in the tropical Pacific and long-term human activities jointly drove the rise in ocean temperatures, causing global ocean temperatures to soar to their highest levels for the first time. Although corals can recover from brief bleaching events, prolonged thermal stress can lead to their death. NOAA has raised the coral bleaching threat level in parts of the Caribbean to 5, a new highest level, indicating that the corals in the region are at risk of "nearly complete mortality."
2)【学术】气候变化对海洋基础物种的影响
海洋基础物种是全球沿海生态系统的生物基础,它们为众多生物提供结构性栖息地、食物和保护,同时也提供多种生态系统服务。《海洋科学年度综述》期刊发布文章指出,气候变化对这些基础物种及其支持的生态系统构成了重大威胁。文章回顾了气候变化对常见海洋基础物种(包括珊瑚、海带、海草、盐沼植物、红树林和双壳类动物)的影响。研究表明,全球变暖及其带来的热浪和海平面上升,不仅导致所有海洋基础物种及其相关群落数量大幅下降,而且导致许多物种分类单元和生物地理区域的范围向极地迁移,甚至被改变为几乎不提供任何固着物种覆盖的区域,或被较小且快速生长的物种所取代。这些影响还包括基础物种与其他物种的相互作用发生改变,这些变化对相关群落、生物多样性和生态系统功能产生了连锁效应。
【Academics】Impacts of Climate Change on Marine Foundation Species
Marine foundational species are the biological foundation of coastal ecosystems worldwide. They provide structural habitats, food, and protection for numerous organisms, while also offering various ecosystem services. The article points out that, climate change poses a significant threat to these foundational species and the ecosystems they support. The article reviews the impact of climate change on common marine foundational species, including corals, kelp, seagrasses, salt marsh plants, mangroves, and bivalves. Research indicates that global warming, along with the heatwaves and rising sea levels it brings, not only leads to a significant decline in the number of all foundational marine species and their associated communities but also causes many taxonomic units and biogeographic regions to shift poleward. In some cases, these regions are transformed into forms that provide almost no cover of sessile species or are replaced by smaller, rapidly growing weedy species. Research indicates that these impacts also include changes in the interactions between foundational species and other species, which have cascading effects on related communities, biodiversity, and ecosystem functions.
3)【学术】未来的大气河流(AR)可能会导致西海岸附近海平面灾难性上升
气候专家小组利用过往大气河流的形成及其对加利福尼亚州、俄勒冈州和华盛顿州部分地区的影响的数据创建了一个模型,试图预测在全球变暖的情境下,大气河流着陆处的海岸线周围未来海平面上升情况。模型研究表明,由于全球变暖的影响,未来在太平洋形成的大气河流到达北美西海岸时可能会导致沿海岸线的海平面上升200%。这种上升类似于飓风引起的风暴潮,再加上与大气河流相关的大量降雨,可能会给加利福尼亚海岸的社区带来灾难性的影响。模型研究还显示,加州不同地区的海平面可能会出现不同程度的海平面上升,南部可能会比北部地区更高。
【Academics】Future atmospheric rivers(AR) could bring catastrophic ocean level rise off the West Coast
A group of climate experts created a model using data from past AR formations and their impact on parts of California, Oregon, and Washington to try to predict the future sea level rise along the coastlines where ARs make landfall under global warming scenarios. Model studies indicate that due to the impact of global warming, future ARs forming in the Pacific may cause sea levels along the North American West Coast to rise by up to 200% when they arrive. This rise, similar to storm surges caused by hurricanes, combined with the heavy rainfall associated with ARs, could have catastrophic effects on communities along the California coast. Model studies also show that sea levels in different regions of California may rise to varying degrees, with the southern regions potentially experiencing higher increases than the northern ones.
4)【观点】安东尼奥·古特雷斯(联合国秘书长):海平面上升加速,太平洋岛屿气候风险加剧
联合国秘书长安东尼奥·古特雷斯访问汤加,并出席了太平洋岛屿论坛领导人会议。在会议上,古特雷斯警示说,海平面上升速度至少是过去3000年来最快的,这些岛屿国家正面临着被不断上升的海水吞噬的危险。古特雷斯强调,如果全球气温比工业化前水平上升超过1.5摄氏度,海平面上升可能会成为更严重的威胁。他表示,随着气温上升2摄氏度,一些气候模型预测格陵兰冰盖和部分西南极冰盖可能比预期更快地崩塌。联合国和世界气象组织发布的报告均显示由于气候变暖导致海平面上升,再加上冰川和冰盖融化,许多太平洋岛屿国家可能会遭受更频繁的洪水。古特雷斯认为G20国家是主要的排放国,且具有最大的领导能力和责任,有义务立即采取行动,为全球约80%的温室气体排放负责,并强调将全球变暖限制在1.5摄氏度以内是防止这些灾难性后果的唯一途径。
【Perspectives】 António Guterres, UN Secretary-General: Pacific Islands Climate Risk Growing as Sea Level Rise Accelerates
United Nations Secretary-General António Guterres visited Tonga and attended the Pacific Islands Forum Leaders' Meeting. At the meeting, Guterres warned that these island nations are facing the danger of being engulfed by rising seawater, as the sea level is rising at the fastest rate in at least 3,000 years. Guterres emphasized that if global temperatures rise more than 1.5 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels, sea level rise could become a more severe threat. He stated that as temperatures rise by 2 degrees Celsius, some climate models predict that the Greenland ice sheet and parts of the West Antarctic ice sheet may collapse faster than expected. Additionally, reports released by the United Nations and the World Meteorological Organization indicate that due to climate warming causing sea level rise, coupled with the melting of glaciers and ice caps, many Pacific island nations may experience more frequent flooding. Guterres believes that the G20 are the largest emitters and have the greatest leadership and responsibility, therefore they have an obligation to take immediate action, being responsible for approximately 80% of global greenhouse gas emissions, and emphasizes that limiting global warming to within 1.5 degrees Celsius is the only way to prevent these catastrophic consequences.
5)【资源】报告揭示研究海洋酸化对海洋生物的影响的迫切需要
“重返蓝色(Back to Blue)”倡议近期发布报告称关于海洋酸化和海洋生物之间直接因果关系的研究可以为政策制定者提供制定政策的依据,但目前关于这方面的研究较为缺乏。报告指出,2022年联合国《生物多样性公约》第15届会议呼吁采取行动“尽量减少气候变化和海洋酸化对生物多样性的影响”,但目前已知的应对海洋酸化的政府级行动计划只有13项。报告提出研究多在实验室进行,缺乏实地数据,这可能导致措施偏离方向,甚至造成意外后果。因此报告强调需要投入大量资金进行海洋酸化的研究,以收集更确凿的数据,推动基于科学证据的国家行动计划的制定。
【Resources】Research proving impact of ocean acidification on marine life urgently needed: Report
The "Back to Blue" initiative recently released a report stating that research on the direct causal relationship between ocean acidification and marine organisms can provide a basis for policymakers to formulate policies, but currently, there is a lack of research in this area. The report points out that the 15th meeting of the United Nations Convention on Biological Diversity in 2022 called for action to "minimize the impact of climate change and ocean acidification on biodiversity," but currently, there are only 13 known government-level action plans to address ocean acidification. The report suggests that most research is conducted in laboratories, lacking field data, which may lead to measures going off course or even causing unintended consequences. Therefore, the report emphasizes the need to invest significant funds in ocean acidification research, in order to collect more conclusive data and promote the development of science-based national action plans.
6)【观点】40多位气候科学家:全球变暖可能导致大西洋经向翻转环流(AMOC)发生重大变化
超过40位气候科学家警示北欧部长们,全球变暖可能导致大西洋经向翻转环流(AMOC)发生重大变化,这可能会引发天气模式的急剧变化和生态系统的破坏。AMOC是一个将暖水输送到北大西洋并为欧洲提供温和气候的洋流系统,其崩溃可能会危及北极地区及以外居民的生活条件。科学家们在给包括丹麦和瑞典在内的北欧部长理事会的信中表示,AMOC的变化将对北欧国家乃至世界其他地区产生毁灭性和不可逆转的影响。信中敦促理事会采取行动,包括呼吁全球减少温室气体排放。其中一位科学家彼得·迪特莱夫森(哥本哈根大学教授)表示如果英国和爱尔兰变得像挪威北部那样,将会产生严重后果,而且这种可能性不低。
【Perspectives】More than 40 climate scientists warn Nordic ministers of changing Atlantic Ocean current
More than 40 climate scientists have warned Nordic ministers that global warming could lead to significant changes in the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC), which could trigger abrupt changes in weather patterns and the disruption of ecosystems. The AMOC is a current system that transports warm water to the North Atlantic and provides a temperate climate for Europe. Its collapse could jeopardize the living conditions of residents in the Arctic region and beyond. Scientists, in a letter to the Nordic Council of Ministers, which includes Denmark and Sweden, stated that the AMOC will have devastating and irreversible impacts on Nordic countries and other parts of the world. The letter urges the council to take action, including calling for a global reduction in greenhouse gas emissions. One of the scientists, Peter Ditlevsen (a professor at the University of Copenhagen), stated that if the UK and Ireland were to become like northern Norway, it would have severe consequences, and the likelihood of this happening is not low.
查看/view
7)【解读】新工具提供了对沿海社区福祉的洞察
美国海洋和大气管理局下的渔业局(NOAA Fisheries) 推出了一个新的社区环境公正探索者网络工具,该工具描述了美国近5000个沿海社区的环境公正问题。该工具通过可视化指标,例如渔业依赖和贫困,创建了一个仪表板,用于探索和比较沿海社区可能面临的不同压力。该工具旨在帮助管理者、研究人员和公众理解环境公正问题,支持社区自我教育、参与决策,并督促政府负责。它还支持NOAA Fisheries的持续社会指标工作和美国海洋公正战略,帮助实现NOAA Fisheries的公平和环境公正战略目标,并支持与社会影响、环境公正、基于生态系统的渔业管理、自然灾害和气候变化相关的法定环境公正分析和评估。
【Interpretation】New Tool Provides Insight into Coastal Community Well-Being
NOAA Fisheries has launched a new Community Environmental Justice Explorer Network tool that describes environmental justice issues in nearly 5,000 coastal communities across the United States. The tool creates a dashboard using visualized indicators, such as fishery dependence and poverty, to explore and compare the different pressures that coastal communities may face. This tool is designed to help managers, researchers, and the public understand environmental justice issues, support community self-education, engage in decision-making, and hold the government accountable. It also supports NOAA Fisheries' ongoing social indicators work and the U.S. Ocean Justice Strategy, helping to achieve NOAA Fisheries' equity and environmental justice strategic goals, and supports statutory environmental justice analyses and assessments related to social impacts, environmental justice, ecosystem-based fisheries management, natural disasters, and climate change.
海洋治理
关键点
- 彭博慈善基金会等呼吁保护海洋需要行动而非更多承诺:全球海洋保护现状堪忧,目前仅有8.3%的海洋得到了有效保护,按照当前的保护速度,到2030年将仅有9.7%的海洋会得到保护。为实现海洋保护目标,全球北方国家必须以身作则,需要在自身水域恢复退化的生态系统,并通过财政和能力建设投资于国外的保护工作。
- 公海联盟发布报告介绍内陆国家在公海生物多样性保护中的利益与机遇。报告指出,《BBNJ协定》使各缔约方能够公平公正地分享千年发展目标的惠益,通过建立财务机制与能力建设和海洋技术转让委员会来支持内陆国家的能力建设和海洋技术发展,内陆国家可以通过划区管理工具和环境影响评估来维护全球海洋利益。
- 皮尤慈善信托基金会指出,世贸组织成员国正在努力加强2022年6月通过的渔业补贴协定,以限制导致非法捕捞和过度捕捞的补贴,这对实现全球生物多样性框架目标(目标18)至关重要,有助于改善海洋健康、恢复鱼类资源和保障数百万人的生计。
红树林浅滩上的一只鲨鱼|Anita Kainrath/Ocean Image Bank.
1)【观点】Antha Williams(彭博慈善基金会环境项目的负责人)和 Enric Sala(“原始海洋”的创始人兼执行董事):海洋需要行动,而不是更多的承诺
全球变暖对海洋造成了严重影响,包括珊瑚礁的破坏和海洋生物种群的减少。高度保护且管理良好的海洋区域(MPA)有助于恢复海洋生态系统,保障数十亿依赖健康海洋的人们的食物安全和生计。彭博海洋基金会资助的一个非政府组织合作伙伴团体发布的一项新报告提出,全球只有8.3%的海洋得到了这种保护,而且大多数MPAs要么保护力度弱,要么只是名义上的保护,并指出只有14个国家将其水域的30%或更多的水域指定为保护区,按照这种当前的保护速度,到2030年只有9.7%的海洋会得到保护。Antha Williams和Enric Sala提出,全球北方国家必须以身作则,需要在自己的水域恢复退化的生态系统,并通过财政和能力建设投资于国外的保护工作。另外,为了实现海洋保护的“30×30”目标,并确保长期的环境和经济回报,政府需要采取五项关键行动,这包括增加国家和国际水域的MPAs数量、实施和积极管理MPAs、发达国家为发展中国家提供财政支持、收集标准化数据以监控进展,以及承认和恢复原住民的权利。
【Perspectives】Antha Williams (leader of the environment program at Bloomberg Philanthropies) and Enric Sala (founder and executive director of Pristine Seas): the ocean needs action, not more promises
Global warming is having a serious impact on the oceans, including the destruction of coral reefs and the decline of marine populations. Well-managed and highly protected marine areas (MPAs) help restore marine ecosystems and guarantee food security and livelihoods for billions of people who depend on healthy oceans. However, a new report released by a consortium of NGO partners funded by the Bloomberg Oceans Foundation suggests that only 8.3 percent of the world's oceans have such protection and that most MPAs are either weakly or nominally protected, noting that only 14 countries have designated 30 percent or more of their waters as protected areas and that at this current rate of protection, only 9.7% of global oceans could be protected by 2030. Antha Williams and Enric Sala suggest that countries in the Global North must lead by example and need to restore degraded ecosystems in their own waters and invest in conservation efforts with foreign countries through finance and capacity building. In addition, in order to achieve the 30 x 30 targets for marine conservation and ensure long-term environmental and economic returns, governments need to take five key actions, which include increasing the number of protected areas in national and international waters, implementing and actively managing MPAs, providing financial support from developed countries for developing countries, collecting standardized data to monitor progress, and recognizing and restoring the rights of indigenous peoples.
2)【资源】《BBNJ协定》:内陆国家的利益与机遇
2023年6月19日,联合国通过了《BBNJ协定》,该协定自2023年9月20日起开放供各国签署,并将持续开放两年。《BBNJ协定》的目标是保护国家管辖范围外区域(ABNJ)的海洋生物多样性,并且纳入了对内陆国家,特别是内陆发展中国家的特殊考虑。首先,《BBNJ协定》使各缔约方能够公平公正地分享千年发展目标的惠益,这包括货币和非货币惠益;其次,《BBNJ协定》通过建立财务机制与能力建设和海洋技术转让委员会来支持内陆国家,尤其是内陆发展中国家的能力建设和海洋技术发展;最后,内陆国家可以通过划区管理工具和环境影响评估来维护全球海洋利益。《BBNJ协定》需要60个国家签署才能生效,内陆国家可以尽早加入《BBNJ协定》,为协定的早日生效与实施做出贡献,推动协定制度和流程的发展。早期缔约方的问题和优先事项可以得到充分探讨和听取。BBNJ缔约方在加入协定后,可以积极参与筹委会(Preparatory Committee)议程,通过与其他内陆国家和内陆发展中国家的非正式对话和闭会期间的会议来坚定其立场。
【Resources】High Seas Treaty: benefits and opportunities for landlocked countries
On 19 June 2023, the international community adopted the Treaty on the High Seas (BBNJ Agreement), which has been open for signature by all States since 20 September 2023 and will remain so for a further two years. The objectives of the BBNJ Agreement are to conserve the ABNJ's marine biodiversity and incorporates special considerations for landlocked countries, particularly LLDCs. Firstly, the BBNJ Agreement enables parties to share fairly and equitably in the benefits of the MDGs, which include both monetary and non-monetary benefits; secondly, the BBNJ Agreement supports capacity-building and marine technology development in landlocked countries, particularly LLDCs, through the establishment of a financial mechanism and a dedicated committee on capacity-building and transfer of marine technology; and lastly, landlocked countries can safeguard global ocean interests through area-based management tools and environmental impact assessments. Since the BBNJ Agreement requires 60 signatories to enter into force, early accession by landlocked countries to the BBNJ Agreement can contribute to its early entry into force and implementation, and promote the development of the Agreement's regime and processes. Moreover, the issues and priorities of the early parties can also be adequately represented and heard. Upon accession to the agreement, the BBNJ parties should actively participate in the Preparatory Committee process and firm up their positions through informal dialogues and intersessional meetings with other landlocked countries and LLDCs.
3)【观点】皮尤慈善信托基金会:世贸组织协定有助于保障未来海洋生物的多样性
在2022年12月达成的“昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架”中,196个国家承诺到2030年共同保护地球30%的海洋、陆地和淡水资源,即“30×30目标”,并消除对生物多样性有害的补贴。世贸组织(WTO)成员国正在努力加强2022年6月通过的渔业补贴协定,以限制导致非法捕捞和过度捕捞的补贴。但是目前超过三分之一的全球鱼类资源被过度开发,而政府每年向捕鱼业提供约220亿美元的补贴,加剧了过度捕捞和生物多样性损失。要想实现生物多样性框架内的目标18,即以适度、公正、公平和平等的方式消除、逐步淘汰或改革损害生物多样性的激励措施,包括政府补贴,各国政府必须在 2025 年前明确对生物多样性有害的激励措施,在 2030 年前彻底消除这些激励措施,或逐步减少这些激励措施。世贸组织成员于2022年同意制定更多条款来解决尚未解决的问题,包括采取措施解决导致过度捕捞和产能过剩的补贴问题,目前,尽快达成关于渔业补贴的协定,确定附加规则,将使全球更接近实现上述目标,特别是目标 18,有助于改善海洋健康、恢复鱼类资源和保障数百万人的生计。
【Perspectives】Pew Charitable Trust: WTO Deal Could Help Secure the Future of Ocean Biodiversity
In the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework, agreed in December 2022, 196 countries committed to collectively conserve 30 percent of the planet's ocean, land and fresh water by 2030, known as the‘30 by 30’, and to eliminate subsidies that harm biodiversity. Members of the World Trade Organization (WTO) work toward strengthening a fisheries subsidies agreement that was adopted in June 2022 to limit subsidies that lead to illegal fishing and overfishing. But more than one-third of fish stocks worldwide are exploited beyond sustainable levels, and government subsidies to the fishing industry, amounting to some $22 billion annually, exacerbate overfishing and biodiversity loss. To achieve Target 18 within the biodiversity framework to eliminate, phase out or reform incentives, including government subsidies, that harm biodiversity – and to do so in a proportionate, just, fair and equitable way, governments must identify biodiversity-harming incentives by 2025 and either completely eliminate them or phase them down by 2030. WTO members agreed in 2022 to develop additional provisions to address outstanding issues, including measures to address subsidies that contribute to overfishing and overcapacity, and for now, reaching an agreement on fisheries subsidies as soon as possible and identifying additional rules will bring the world closer to achieving the Global Biodiversity Framework's targets by 2030, in particular Target 18, which contributes to improving the health of the oceans, restoring fish stocks and safeguarding the livelihoods of millions of people who depend on them.
4)【资源】报告介绍南大洋的变化以及保护南大洋所需的措施
南大洋对气候变化的响应是全球最快的,再加上人类活动的影响,南极生态系统承受着诸多压力。目前,海洋保护区、昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架以及南极海洋生物资源保护委员会构成了南大洋海洋保护的基础。南极和南大洋联盟(ASOC)发布报告,重点介绍了南大洋的变化以及保护南大洋所需的措施。报告首先指出南大洋面临的现状和保护进展。报告介绍了气候变暖、海冰波动加剧、海洋酸化、极端天气事件增多、物种变化、磷虾渔业增加、旅游业增长和塑料污染这些南大洋当前面临的挑战,还讨论了南极洲的管理问题,这包括南极条约体系,南极海洋生物资源保护公约、南极海洋生物资源保护委员会在实现“30x30”目标中的作用与承诺以及亚南极岛屿海洋保护区。报告列出了四个可以为“30x30”目标做出重大贡献但还未建立起来的海洋保护区,即威德尔海第一阶段海洋保护区、东南极海洋保护区、南极半岛海洋保护区和威德尔海第二阶段海洋保护区,它们将覆盖26%的南大洋和近3%的全球海洋,会是历史上最大的海洋保护行动。报告强调南极海洋生物资源保护委员成员必须遵循风险预防原则,为南极的利益进行合作,并采取行动,以保护南极海洋生态系统,应对气候变化和人类活动增加带来的挑战。
【Resources】A report clarifies the changes in the Southern Ocean and the measures needed to protect it
the response of the Southern Ocean to climate change is the fastest on Earth and that, combined with the impacts of human activities, Antarctic ecosystems are under many pressures. Currently, marine protected areas, the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework and the Commission for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources (CCAMLR) form the basis for marine conservation in the Southern Ocean. The Antarctic and Southern Ocean Coalition (ASOC) released a report focusing on changes in the Southern Ocean and the measures needed to protect it. The report begins by noting the current situation facing the Southern Ocean and the conservation process. The report introduces the challenges currently facing the Southern Ocean, including climate warming, increased sea ice fluctuations, ocean acidification, more frequent extreme weather events, species changes, increased krill fisheries, tourism growth, and plastic pollution. It also discusses the management issues of Antarctica, including the Antarctic Treaty System, the Convention on the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources, the role and commitments of the Commission for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources(CCAMLR) in achieving the 30x30 target, and sub-Antarctic islands in the Southern Ocean. The report lists four MPAs that could make a significant contribution to the 30x30 goal but have not yet been established, namely, the Weddell Sea Phase 1 & 2 MPAs, Domain 1 MPA and East Antarctic MPA, which would cover 26 percent of the Southern Ocean and nearly 3 percent of the global ocean, and represent the largest marine conservation effort in history. The report emphasizes the need for CCAMLR members to follow the precautionary principle, to cooperate for the benefit of Antarctica and to take action to protect Antarctic marine ecosystems in the face of the challenges posed by climate change and increased human activity.
5)【资源】马尔代夫呼吁缔约方考虑在《濒危野生动植物种国际贸易公约》(CITES)第二十届缔约方大会上加强对鲸鲨的保护
马尔代夫共和国最近向《濒危野生动植物种国际贸易公约》第二十届缔约方大会提交了一份提案,要求将鲸鲨从CITES附录2转移到附录1。这是基于鲸鲨在过去三代中全球种群数量下降了40%-92%的考虑,而且国际自然保护联盟将其列为“濒危物种”。提案指出鲸鲨面临的主要威胁包括捕捞、非法贸易、船只撞击和栖息地退化。马尔代夫请求各缔约方提供有关鲸鲨保护状况、国内外贸易以及非法贸易的信息,并在2024年11月30日前直接回复给马尔代夫的CITES管理机构。提案还介绍了鲸鲨的生物学特性、分布、重要性及其目前的生存状况,说明了将鲸鲨列为附录1物种的科学和保护理由。
【Resources】Maldives Calls for Range State Input: Increased Whale Shark Protection at CITES CoP20
The Republic of Maldives recently submitted a proposal to the 20th Conference of the Parties to the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES) to transfer whale sharks from CITES Appendix II to Appendix I. This is based on the consideration that the global population of whale sharks has declined by 40%-92% over the past three generations, and the International Union for Conservation of Nature has listed them as "endangered species". The proposal points out that the main threats to whale sharks include fishing, illegal trade, ship strikes, and habitat degradation. The Maldives requests all parties to provide information on the conservation status of whale sharks, domestic and international trade, and illegal trade, and to respond directly to the Maldives' CITES Management Authority by November 30, 2024. The proposal also introduces the biological characteristics, distribution, importance, and current survival status of the whale shark, explaining the scientific and conservation reasons for listing the whale shark as an Appendix I species.
查看/view
6)【学术】海藻养殖提供的生态系统服务:现状、知识空白、限制及在欧洲实现最大潜力的未来需求
《渔业科学与水产养殖评论》期刊近期发布文章,评估了海藻养殖在欧洲能够提供的生态系统服务(ES),包括海藻养殖系统的潜在商业价值以及环境、社会、政治和文化影响。文章揭示了海藻养殖带来的三大生态系统服务,即调节和维护(水质等)、供给(食品等)和文化(教育等),还贡献于联合国框架下的许多可持续发展目标,比如目标11(可持续城市和社区)、目标12(负责任的生产和消费)等。文章还提出了海藻养殖潜在的负面影响,比如改变邻近的群落和改变浮游植物的浓度。文章呼吁采取风险管理方法,进行更多的科学研究,并以适当的法规和政策框架为辅助,来支持欧盟该行业的稳步发展。
【Academics】Ecosystem Services Provided by Seaweed Cultivation: State of the Art, Knowledge Gaps, Constraints and Future Needs for Achieving Maximum Potential in Europe
The journal "Reviews in Fisheries Science & Aquaculture" recently published an article evaluating the ecosystem services (ES) that seaweed farming can provide in Europe. The ES aims to assess the potential commercial value of seaweed farming systems as well as their environmental, social, political, and cultural impacts. The article reveals the three major ecosystem services (ES) brought by seaweed farming: regulation and maintenance (such as water quality), provisioning (such as food), and cultural (such as education). It also addresses many of the Sustainable Development Goals under the United Nations framework, such as Goal 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities) and Goal 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production). The article also mentions the potential negative impacts of seaweed farming, such as altering nearby communities and changing phytoplankton concentrations. The article calls for the adoption of risk management approaches, more scientific research, and the support of appropriate regulatory and policy frameworks to ensure the steady development of this industry in the EU.
查看/view
划区管理
关键点
- 彭博海洋倡议指出,为了快速有效实现“30x30”目标,各国政府可以采取更有效的保护措施,包括禁止工业捕鱼、采矿和石油开采等活动,提供足够的资金支持,与原住民和当地社区进行密切合作。
- 法国可持续发展研究所(IDDRI)发表文章指出,监测、控制和监督(MCS)系统的发展对于公海保护区的成功至关重要。MCS技术(包括卫星技术和人工智能)通过优化资源分配和提供对海上可疑非法活动的实时观察,可以为未来公海保护区的管理提供显著的附加价值。技术本身不足以确保MCS的有效性,还需要配套的政策和技术措施,比如促进海上巡逻合作、加强港口国控制、确保有效信息共享等。未来国家可以借助进一步创新的成本低、效益高的MCS来克服公海保护区的管理挑战。
- 法国可持续发展研究所(IDDRI)发表文章指出,编制公海保护区提案必须考虑包括行政监督、MCS、科学活动及教育宣传在内的成本和长期融资问题,以确保其有效性。其中,行政监督以及MCS通常占据预算中主要部分,建议国家和其他非国家行为体在筹备提案时,根据每个地点的特点来提前考虑成本问题,并确定最理想的预算选择,以优化和共享成本。
Laamu Gan Bodu Fendandu海洋保护区|Saltandsunny/Instagram
1)【解读】纠正航向:让“30×30”海洋目标回到正轨
2022年在《生物多样性公约》第十五次缔约方大会上通过的《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》(GBF)承诺到2030年保护世界上30%的陆地和海洋。虽然距离“30x30”的最后期限还有六年时间,但是目前世界上仅有8.3%的海洋受到保护,自GBF通过以来,保护比例仅增加了0.5%,如果按照这种速度发展,到2030年只有9.7%的海洋可以受到保护,这与30%的目标相差甚远。因此,为了快速有效实现“30x30”目标,政府应该采取更有效的保护措施,包括禁止工业捕鱼、采矿和石油开采等活动;提供足够的资金支持,其中发达国家必须为实现GBF设定的到2030年每年至少筹集2000亿美元的目标负责,到2025年每年向发展中国家提供200亿美元,到2030年则提升至每年300亿美元,而发展中国家每年则要拨款680亿美元;协作是关键,必须与原住民和当地社区进行密切合作。
【Interpretation】 Course Correction: Putting the 30x30 Ocean Target Back on Track
The Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (GBF), adopted in 2022 at the 15th Conference of the Parties to the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD), commits to protect and conserve 30 percent of the world's land and oceans by 2030. Although the 30x30 deadline is six years away, only 8.3 percent of the world's oceans are currently protected, with protection increasing by only 0.5 percent since the adoption of the GBF, and if it continues at this rate, only 9.7 percent of the oceans could be conserved by 2030, which is a far cry from the 30 percent target. Therefore, in order to achieve the 30x30 target quickly and effectively, governments should take steps to adopt more effective protection, which includes banning activities such as industrial fishing, mining and oil extraction; and providing sufficient financial support, with developed countries being responsible for achieving the GBF's target of annual $200 billion by 2030, donating $20 billion to developing countries annually by 2025, and increasing it to $30 billion annually by 2030, while developing countries must allocate $68 billion annually; and collaboration is key, with close cooperation with indigenous and local communities.
2) 【学术】新兴技术将在未来公海保护区的监测、控制和监督系统中发挥什么作用?
确保未来公海保护区成功的一个关键条件是发展对人类活动有效的监测、控制和监督(MCS)系统。在过去的十年中,MCS技术迅速发展,包括卫星技术和人工智能,这些技术由各利益相关方提供,包括公司和非营利组织,通过优化资源分配和提供对海上可疑非法活动的实时观察,可以为未来公海保护区的管理提供显著的附加价值。当然,技术本身不足以确保MCS的有效性,还需要配套的政策和技术措施,比如解决能力差距、促进海上巡逻合作、加强港口国控制、改革国家司法系统和确保有效信息共享等。未来国家可以借助进一步创新的成本低、效益高的MCS来克服公海保护区的管理挑战。
【Academics】Monitoring, control and surveillance of future high seas MPAs: what role for emerging technologies?
A key condition for ensuring the success of future high seas MPAs is the development of effective monitoring and control (MCS) of human activities. The rapid development of MCS technologies over the past decade, including satellite technology and artificial intelligence, provided by a variety of actors, including companies and non-profit organizations, can provide significant added value to the management of future high seas MPAs by optimizing resource allocation and providing real-time insights into suspected illegal activities at sea. Of course, technology on its own is not sufficient to ensure the effectiveness of MCS, and complementary policy and technical measures are needed, such as addressing capacity gaps, promoting maritime patrol cooperation, strengthening port state control, reforming national judicial systems and ensuring effective information sharing. In the future, states can overcome the challenges of managing MPAs on the high seas with the help of further innovative cost-effective MCS.
3)【学术】评估未来公海保护区的管理成本:初步方法论
编制公海保护区(HSMPA)提案,必须考虑其成本和长期融资问题,否则会危及其有效性与国际声誉。公海管理成本主要有四种类别:行政和监督;监测、控制和监督(MCS);科学活动;教育和宣传。在行政与监督中,政府对于合作、集中或分散治理结构的选择、行政结构与行政人员来源这三个因素会对成本产生影响;在MCS中,对私营MCS公司的采用、非营利组织的支持、国家的实物捐助以及HSMPA的区域划分程度都会对管理成本产生影响;在科学活动中,科研目标水平、科研方法、与相关国际组织的协调以及与私营部门的合作也会影响管理成本;在教育与宣传中,由于地理位置的限制,HSMPA的教育推广活动可能比沿海海洋保护区的有限得多。其中,行政和监督以及MCS通常是预算中占比最大的部分,建议国家和其他非国家行为体在准备HSMPA时,根据每个地点的特点来提前考虑成本问题,并确定最理想的预算选择,以优化和共享成本。
【Academics】Assessing the management costs of future high seas marine protected areas: an initial methodological approach
When preparing a proposal for a High Seas Marine Protected Area (HSMPA), it is important to consider its costs and long-term financing, as failure to do so could jeopardize its effectiveness and international reputation. There are four main categories of high seas management costs: administration and oversight; monitoring, control and surveillance (MCS); scientific activities; education and outreach. In administration and oversight, three factors affect costs: the government's choice of cooperative, centralized or decentralized governance structure, the office structure and staffing; in MCS, the use of private MCS companies, the support of non-profit organizations, in-kind contributions from state, and the degree of zoning of the HSMPA; and in scientific activities, the level of ambition, the methodology, coordination with relevant international organizations, and cooperation with the private sector also affect management costs; in education and outreach, educational outreach activities in HSMPAs may be much more limited than in coastal MPAs due to geographic constraints. Of these, administration and oversight, and MCS are usually the largest part of the budget, and it is recommended that states and other non-state actors prepare for HSMPAs by considering costs in advance based on the characteristics of each site and identifying the most desirable budgetary options to optimize and share costs.
4)【观点】斯蒂芬·伍德利(IUCN世界保护区委员会科学和生物多样性组副主席、OECM专家组联合主席):如何识别海洋OECM
在《生物多样性公约》缔约方大会第十六次会议(COP16)上,斯蒂芬·伍德利博士详细介绍了关于OCEM的一系列问题。伍德利博士首先明确了《生物多样性公约》对OECM的定义及其四项重要准则,澄清了OECM与可持续利用区和保护地的区别,阐述了IUCN开发的一个通过初步筛选、知情同意和对所有类别和准则进行全面评估等来识别OECM的工具,并重点介绍了业内讨论较多的识别OECM的八项标准中的第四、五、六项标准。根据这些识别标准, 伍德利博士按照治理类型,指出海洋OECM可能包括:政府管辖海域、原住民和当地社区管辖的海域、私营机构治理的海域和行业机构治理的海域,并讨论了水产养殖区、单一物种措施、渔业管理区和海洋垂直分区等潜在OECM类型的常见问题,同时强调了实现生物多样性保护不仅需要关注行动目标3,即保护30%的陆地和海洋,还需要全面实施《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》中的所有23个行动目标。
【Perspectives】Stephen Woodley (Vice Chair for Science and Biodiversity and Co-Chair OECM Specialist Group World commission on Protected Areas, lUCN): How to Identify Marine OECMs
At the sixteenth meeting of the Conference of the Parties to the Convention on Biological Diversity (COP16), Dr. Stephen Woodley gave a detailed presentation on a range of issues concerning OCEM. Dr. Woodley began by clarifying the CBD's definition of OECM and its four key criteria, clarifying the difference between OECMs and Sustainable Use Areas and Protected Areas, describing a tool developed by the IUCN to identify OECMs through initial screening, informed consent, and a comprehensive assessment of all categories and criteria, and highlighting the fourth, fifth, and sixth criteria among the eight standards for identifying OECM that are frequently discussed in the industry based on these identification criteria. Dr. Woodley identified, by type of governance, that marine OECMs may include: government-governed marine areas, areas under the jurisdiction of aboriginal and local communities, areas under the governance of private institutions, and areas under the governance of industry bodies, and discussed common problems with OECMs such as aquaculture zones, single-species measures, fisheries management zones, and vertical zonation of oceans and seas, as well as emphasizing the fact that for achieving biodiversity conservation, there is a need to focus not only on Action Target 3, which is to protect 30 percent of land and sea, but also to fully implement all 23 Action Targets of the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework.
蓝色经济
关键点
- 根据自然资源部,2024年前三季度,我国海洋经济稳中有进,海洋生产总值达到7.7万亿元,同比增长5.4%,其中传统产业和新兴产业均保持增长。海洋资源要素保障和供给能力增强,企业经营状况和预期总体稳定,科技创新能力提升。未来,我国将着力推进现代海洋产业体系建设,推动海洋经济高质量发展。
- 为应对小岛国面临因气候变暖而被海洋淹没的威胁,太平洋和加勒比小岛屿发展中国家联盟(the 6PAC+ Alliance)的代表们紧急呼吁国际海事组织(IMO)实施强制性的全球碳排放税,呼吁对大型商业船舶实施首个全球性的碳排放税,以激励航运业的转型并提供公平的过渡。
- 新贝德福德既是美国最盈利的渔港,也是首个大型海上风电集结港。 新贝德福德港务局对美国海洋能源管理局提出的中大西洋2号区域海上风电开发计划表示担忧,认为该计划可能对当地捕鱼业产生负面影响,强调需要平衡海上风电开发与关键捕鱼区域的保护。

一艘货船驶离巴拿马城的巴拿马运河|Martin Bernetti /AFP via Getty Images
1)【解读】自然资源部:前三季度海洋经济呈现稳中有进态势
自然资源部分析了2024年前三季度海洋经济的运行情况:海洋经济呈现稳中有进的态势。海洋生产总值达到7.7万亿元,同比增长5.4%。海洋传统产业如船舶制造和海洋旅游保持增长,新兴产业如海工装备制造业和海洋药物业也快速发展。海洋资源要素保障和供给能力增强,新增批准用海面积和海洋油气产量均有所增长。企业经营状况和预期总体稳定,创新投入持续增加。海洋对外贸易平稳增长,港口航道不断优化。面对复杂多变的国内外环境,海洋经济在稳中有进的基础上还需进一步巩固,未来将着力推进现代海洋产业体系建设,推动海洋经济高质量发展。
【Interpretations】Ministry of Natural Resources: The marine economy showed a steady and progressive trend in the first three quarters
The Ministry of Natural Resources has interpreted the performance of the marine economy in the first three quarters of 2024: the marine economy shows a steady and progressive trend. The gross marine product reached CNY 7.7 trillion, a year-on-year increase of 5.4%. Traditional marine industries, such as shipbuilding and marine tourism, have maintained growth, while new industries, such as the offshore equipment manufacturing industry and the marine pharmaceutical industry, have also developed rapidly. The security and supply capacity of marine resource elements have been enhanced, with growth in the area of newly approved sea use and marine oil and gas production. The overall business performance and expectations of enterprises are stable, with continuous increases in innovation investment. Marine foreign trade is growing steadily, and port channels are being continuously optimized. In the face of a complex and ever-changing domestic and international environment, the marine economy, while maintaining stability and progress, needs further consolidation. In the future, efforts will focus on advancing the construction of a modern marine industry system and promoting the high-quality development of the marine economy.
查看/view
2)【解读】太平洋和加勒比岛国呼吁对国际航运排放征收首个全球碳税
全球航运业占全球贸易的90%,其产生的温室气体排放量却占全球人类活动排放量的3%,这些排放导致气候变暖,威胁着小岛国的生存,图瓦卢等低洼岛屿可能会在未来50至100年内被海洋完全淹没。为了阻止这种最坏情况的发生,太平洋和加勒比小岛屿发展中国家联盟(the 6PAC+ Alliance)的代表们紧急呼吁国际海事组织(IMO)实施强制性的全球碳排放税,呼吁对大型商业船舶实施首个全球性的碳排放税,每吨航运排放征收150美元,以激励航运业的转型并提供公平的过渡。这项提议的税收将适用于国际运输货物和乘客的船舶,但不包括国内船队。2025年IMO的175个成员国需要对这一提议进行投票,如果被采纳,这将是首个对碳排放进行全球定价的税种。
【Interpretations】Pacific and Caribbean Island Nations Call for the First Universal Carbon Levy on International Shipping Emissions
The global shipping industry accounts for 90% of global trade. Its greenhouse gas emissions account for 3% of total emissions from human activities. These emissions contribute to climate change, threatening the survival of small island nations. Low-lying islands like Tuvalu may be completely submerged by the ocean within the next 50 to 100 years.
To prevent this worst-case scenario, representatives of the 6PAC+ alliance urgently call on the International Maritime Organization (IMO) to implement a mandatory global carbon emissions tax, the world's first global carbon emissions tax on large commercial ships, charging $150 per ton of shipping emissions, to incentivize the transformation of the shipping industry and provide a fair transition. to implement. This proposed tax would apply to ships transporting goods and passengers internationally but would not include domestic fleets. In 2025, the 175 member states of the IMO will need to vote on this proposal. If adopted, it will be the first global tax to price carbon emissions.
3)【解读】新贝德福德港务局对美国海洋能源管理局提议的中大西洋海上风电开发区表示“严重关切”
新贝德福德既是美国最盈利的渔港,也是首个大型海上风电集结港。新贝德福德港务局(下称港务局)对美国海洋能源管理局(下称管理局)提出的中大西洋2号区域的海上风电开发计划表达了严重的担忧。该港务局支持海上风电的开发,但是认为该计划可能会对新贝德福德渔港的捕鱼业产生负面影响。港务局强调,特别是在管理局提议的中大西洋2号区域范围内的关键扇贝捕鱼区域,包括象鼻、哈德逊峡谷和德拉瓦湾,必须平衡海上风电的开发与现有产业的保护。这些区域的十六年捕捞价值估计接近20亿美元,其中近15亿美元来自海扇贝。港务局执行主任戈登·卡尔指出管理局在划定提议区域边界时没有充分利用已有的数据,忽视了这些关键的捕鱼区域。港务局呼吁管理局认真考虑商业捕鱼业的担忧,并采取更负责任和更一致的方法来发展海上风电,以平衡可再生能源的需求和长期存在的商业捕鱼业的需求。
【Interpretations】New Bedford Port Authority Expresses "Grave Concerns" Over BOEM’s Proposed Central Atlantic Offshore Wind Development Area
New Bedford, located in this area, is not only the most profitable fishing port in the United States but also the first large-scale offshore wind assembly port. New Bedford Port Authority has expressed serious concerns about the offshore wind development plan for Mid-Atlantic Area 2 proposed by the U.S. Bureau of Ocean Energy Management (BOEM). NBPA supports the development of offshore wind power but believes that the plan could negatively impact the fishing industry at the New Bedford Fishing Port. NBPA emphasizes the need to balance the development of offshore wind power with the protection of existing industries, particularly in the key scallop fishing areas within the Mid-Atlantic Wind Energy Area 2 proposed by BOEM, including the Elephant Trunk, Hudson Canyon, and Delmarva, where the estimated 16-year catch value is nearly $2 billion, with nearly $1.5 billion coming from sea scallops. NBPA Executive Director Gordon Carr criticized BOEM for not fully utilizing existing data when delineating the proposed area boundaries, overlooking these critical fishing areas. NBPA calls on BOEM to seriously consider the concerns of the commercial fishing industry and adopt a more responsible and consistent approach to developing offshore wind power, balancing the demand for renewable energy with the long-standing needs of the commercial fishing industry.
4)【解读】德国莱茵集团(RWE)和美国国家电网联合提议建设纽约最大的海上风电项目
德国莱茵集团(RWE)和美国国家电网联合提议在纽约州开发一个名为“Empire Wind 2”的海上风电项目,这将是纽约州迄今为止最大的海上风电项目。该项目计划安装超过100台风力涡轮机,预计发电能力将达到1.2吉瓦,足以为超过60万户家庭提供电力。这一提议是纽约州实现其清洁能源目标和减少温室气体排放努力的一部分,旨在推动该州到2035年实现100%清洁电力供应的目标。项目的成功实施可以对纽约州的能源结构产生重大影响,同时促进当地经济发展和就业机会。
【Interpretations】RWE and National Grid Propose New York's Largest Offshore Wind Project
RWE and National Grid are proposing to develop an offshore wind project in New York State called Empire Wind 2, which would be the largest offshore wind project in New York State to date. More than 100 wind turbines are planned to be installed in the project, which is expected to have a generating capacity of 1.2 gigawatts (GW), enough to power more than 600,000 homes. The proposal is part of New York State's efforts to meet its clean energy goals and reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and is intended to advance the state's goal of achieving a 100 percent clean electricity supply by 2035. Successful implementation of the project may have a significant impact on New York State's energy mix while boosting local economic development and employment opportunities.
5)【学术】探索海洋食品生产:可持续和快速生物技术开发的挑战
开发海洋食品技术不仅有助于加强粮食安全和可持续性发展,还有可能改变未来的粮食生产和消费方式。《应用科学》近期发布文章强调,尽管海洋成分具有潜力,但将这些海洋化合物加入食品则面临着提取利用的困难和监管限制的挑战。文章指出,在提取利用的过程中,海洋基质的复杂性增加了提取过程的复杂性,可能导致产量低或生物活性丧失,此外,一旦提取出来,海洋生物活性化合物会面临与配方和产品稳定性有关的挑战。除了提取和利用困难之外,监管限制也面临挑战,为了实现海洋产品商业化,该行业需要严格的产品审批和市场授权要求,但这些要求可能因监管管辖区而异,因此缺乏共同立法使跨多个司法管辖区的公司运营困难。文章指出,采取循环生物基解决方案、采用可持续性评估工具以及通过教育和推广可以有效解决可持续性开发海洋食品的实践问题。文章强调可持续的探索和合作对于未来至关重要,这有助于创造一个有韧性、公平和环保的食品系统。
【Academics】Exploring Marine-Based Food Production: The Challenges for a Sustainable and Fast Biotechnology-Based Development
The development of marine food technologies not only helps to enhance food security and sustainability, but also has the potential to change the way food is produced and consumed in the future. The article recently published by Applied Science highlights that, despite the potential of marine ingredients, the incorporation of these marine compounds into food products is challenged by difficulties in extraction and utilization, as well as regulatory constraints. The article claims that the complexity of the marine matrix adds to the complexity of the extraction and utilisation process, which can lead to low yields or loss of bioactivity, and furthermore, once extracted, marine bioactive compounds face challenges related to formulation and product stability; in addition to difficulties in extraction and utilisation. There are also challenges with regulatory restrictions, and in order for marine products to be commercialised, the industry needs stringent product approval and market authorisation requirements, but these can vary by regulatory jurisdiction, so the lack of common legislation makes it difficult for companies operating across multiple jurisdictions. The article notes that the adoption of circular bio-based solutions, the use of sustainability assessment tools and the adoption of education and outreach can be effective in addressing the practice of sustainable development of marine food products. The article emphasized that sustainable exploration and collaboration were essential for the future, helping to create a resilient, equitable and environmentally friendly food system.
6)【学术】健康饮食与全球水产食品生产
《水产养殖综述》发表文章强调了水产品作为更健康食品选择的重要性。文章提到,尽管全球面临饥饿和营养不良问题,但水产养殖和捕捞渔业提供了一个健康的食品来源,2022年全球水产养殖产量创下新高。文章主张,水产养殖不仅能增加全球鱼类和海鲜产量、减少对野生种群的捕捞压力,还能通过饲料成分选择定制营养成分,以满足消费者健康需求。文章提出,应探索提高养殖物种营养成分的新研究领域,以更好地惠及消费者,特别是在微量营养素缺乏地区的消费者。
【Academics】Healthy Diets and Global Aquatic Food Production
The article published by Reviews in Aquaculture emphasizes the importance of seafood as a healthier food choice. The article mentions that despite the global issues of hunger and malnutrition, aquaculture and capture fisheries provide a healthy food source, with global aquaculture production reaching a record high in 2022. The article argues that aquaculture can not only increase global fish and seafood production and reduce the fishing pressure on wild populations, but also customize nutritional components through feed ingredient selection to meet consumer health needs. The article suggests that new research areas should be explored to enhance the nutritional components of farmed species, in order to better benefit consumers, especially those in regions with micronutrient deficiencies.
查看/view
7)【资源】2024年10月海运市场更新
DHL全球货运公司近期更新了海洋货运市场的报告。报告概述了全球经济前景,强调了通胀下降、货币政策放松和实现软着陆的重要性。尽管经济活动有所下降,但DHL预计黄金周后需求依然强劲。报告还提到了新集装箱船的交付量创历史新高,以及一些承运商正在进行船队更新。运费方面,自7月以来有所下降,但在黄金周后又有所回升,尽管承运商计划在11月提高费率,但高费率的可持续性仍不确定。
【Resources】Ocean Freight Market Update October 2024
DHL Global Forwarding recently updated its report on the ocean freight market. The report outlines the global economic outlook, emphasizing the importance of declining inflation, easing monetary policy, and achieving a soft landing. Despite a decline in economic activity, DHL expects demand to remain strong after the Golden Week.The report also mentioned that the delivery volume of new container ships has reached a record high, and some carriers are updating their fleets. In terms of freight rates, there has been a decline since July, but they have rebounded after the Golden Week. Although carriers plan to increase rates in November, the sustainability of high rates remains uncertain.
查看/view
>> 其他 Others
本快讯为电子月刊,往期内容可以查看这里。如果您在快讯内容或形式上有任何意见或建议,欢迎发邮件至ocean@ghub.org告诉我们,也欢迎您将《蓝色脉搏》推荐给同事和朋友。
 表情
表情
 最热
最热